Surgical approaches to placing breast implants
There are 4 typical approaches to placing breast implants and these will dictate where the incision are made. These are:
- Inframammary placement (incisions are made in the crease under the breast)
- Periareolar placement (incisions are made in the dark skin that encircles the nipple)
- Transaxillary splacement (incisions are made under the arm or in the armpit)
- Transumbilical (a small incision is made in the belly button)

The implant procedure will be discussed with you (method by which the implants will be inserted) as well and any questions you may have will be addressed. All risk and potential complications will be discussed with you too.
Where the incision is made will depend on the type of implant, how much enlargement is being done and other factors of the body. Incisions will be made under the breasts, under the arms or around the nipples.
If you are taking medication, you may be asked to discontinue any (where safe to do so) that may place you at higher risk during surgery in the days or weeks before the procedure. Aspirin and other medications can cause unnecessary bleeding during surgical procedures. If you are a smoker, you will be asked to stop for a period of time before your procedure as this can also cause complications during surgery.
Breast augmentation is an outpatient procedure, but an overnight stay may be required if any complications occur during the surgery. All in all, the surgery can take between 1 and 2 hours. During this time, you will be placed under general anaesthesia and be ‘asleep’ during the entire surgery. This way you will not experience any pain or discomfort associated with the surgical process or have any recollection of the operation. In select cases, a local anaesthesia may be preferred where you will be awake during the procedure, but the breast area will be numbed.
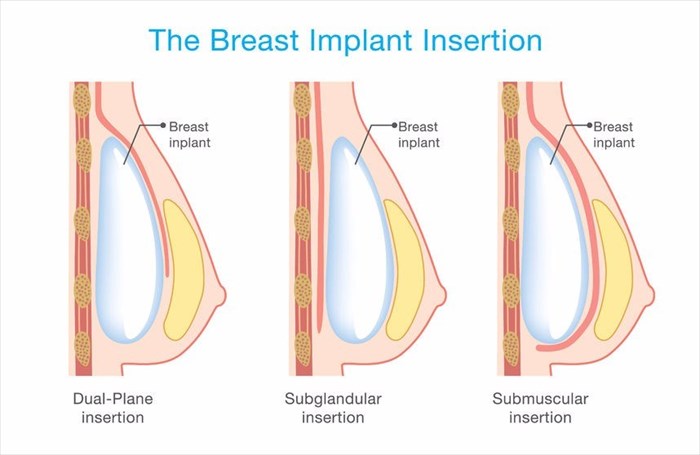
Depending on the manner in which your plastic surgeon has decided to perform the surgery. This may be done in one of two ways:
- Placing the breast implant under the muscle: To do this, your surgeon will separate the breast tissue from the muscles and connective tissue of the chest, creating a pocket either behind or in front of the pectoral muscle. Most surgeons opt for a dual plane implant process where the superior portion of the implant is covered by the muscle and the inferior, beneath the gland.
- Placing the breast implant over the muscle: With this method, the implant will be placed between the chest muscle and breast tissue. This is known as a sub-glandular placement as opposed to the sub-muscular placement described above.
Once in place and the surgeon is satisfied with the position and shape, he or she will close the incisions with stitches (sutures) or surgical tape.