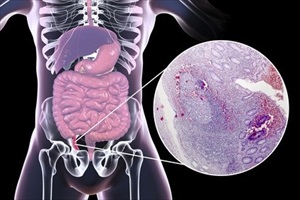
Many medical professionals agree that appendicitis is caused by an obstruction in the appendix, which is classified as either partial or complete. A complete obstruction will be regarded as a medical emergency requiring surgical intervention.
Obstructions are likely caused by an accumulation of faecal matter (hardened stool), inflammation causing a blockage due to tumours, enlarged lymphoid follicles (lymph nodes in the intestines), intestinal worms or other trauma in the body. An obstruction is often linked with bacterial infections, also causing inflammation. Pus forms resulting in increased pressure which causes a person to experience intense pain. If this pain and inflammation compresses blood vessels, blood flow to the appendix is restricted and can result in gangrene.
Faecal matter is highly infectious, and when an appendix bursts can fill the abdominal cavity. Other organs in the body, such as the bladder, sigmoid colon (the part of the large intestine that is closest to the anus and rectum) and caecum (a pouch located where the small and large intestines join), can also become infected.
Any infection in the body causes swelling, which in turn can result in a blockage. The appendix may become infected without bursting. This then results in the formation of an abscess. This is still a serious condition even though infectious material doesn’t leak into the abdominal cavity and remains in the small ‘walled off’ area.
