What are bunions?
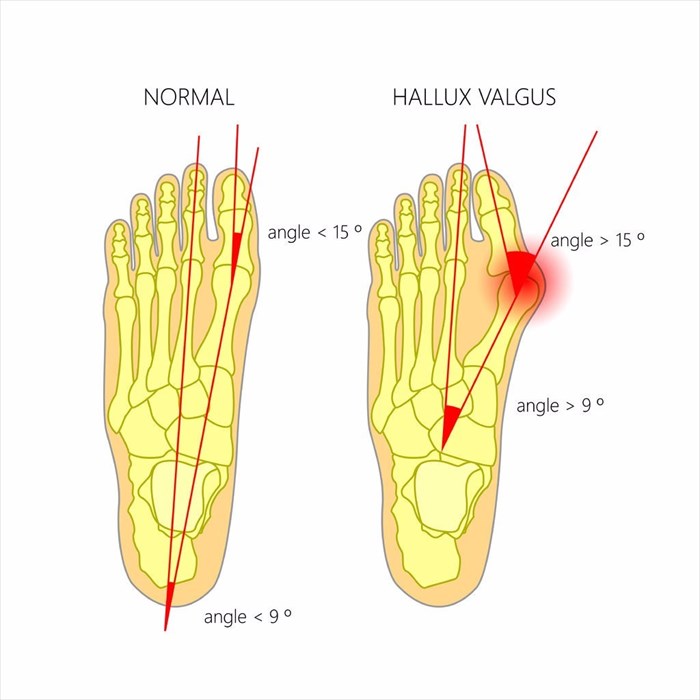
A progressive disorder, bunions (also referred to as hallux valgus – a Latin term > hallux, meaning ‘big toe’, and valgus, meaning ‘turned away from the midline of the body’) develop as a visible bump on the side of the big toe at the base or joint (known as the metatarsophalangeal joint), due to changes in the bony framework of the front portion of the foot.
The result is an inward leaning and rotation of the big toe which no longer points forward but rather turns towards the second toe (this is known as hallux abductovalgus deformity) or sometimes pushes over or under the other toes. Bones in the big toe thus fall out of alignment as the base pushes outwards against the first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ) behind it and creates the characteristic bunion bump.
The bony framework changes of a bunion’s development take place gradually becoming more and more prominent, over the course of a few years.
Once fairly prominent, a person may begin to experience symptoms such as tenderness, stiffness and pain as the toes begin to crowd together. Pain may also be notable when walking, as a pronounced bunion typically takes on the increased pressure of a person’s body weight and the skin around the deformity may become red and inflamed.
Inflammation and redness may also occur due to the swelling of a small fluid-filled sac adjacent to the joint which normally surrounds and cushions it, known as a bursa. This form of inflammation is known as bursitis. Footwear choices also have an impact on the level of discomfort experienced once a bunion has formed (sometimes forming calluses / toughened areas of skin).
Not all who develop bunions, however, experience the above-mentioned symptoms.
The formation of a bunion can result in a potentially permanent deformity and the onset of localised arthritis.
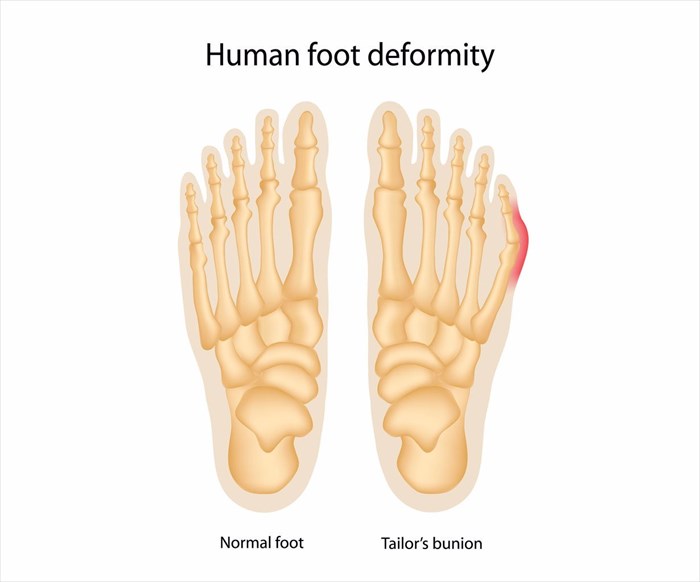
What is a bunionette?
These are smaller, but similar formations to bunions which develop at the joint of the little toe (fifth toe). A bunionette is also known as a tailor's bunion.
Other Articles of Interest

Gout (Gouty Arthritis)
Excess uric acid in the body is one of the main underlying reasons gout (or gouty arthritis) occurs. Learn more about gout, its causes, symptoms and treatment measures...

Down Syndrome
What is Down syndrome and how does it happen? Here's an in depth look at how this genetic condition happens, and how to take the best care of a child born with Down syndrome.

X-rays
X-rays are a very common procedure that many of us have had to have or may have in the future. Learn more about this imaging test...