The following are common deep vein thrombosis complications:
- Post-phlebitic syndrome (post-thrombotic syndrome / PTS): Blood clots can cause damage to the veins and or / valves when blood flow is reduced or slowed down. Effects of this can be seen and felt when blood begins to pool, and is unable to return to the heart. Signs include oedema (persistent or chronic swelling), pain in the affected areas, skin discolouration (often a darkened skin colour) and the development of skin sores (or ulcers). Signs may be mild, but can result in long-term effects such as sores and varicose veins (swollen, twisted and blue veins beneath the skin) if not adequately treated.
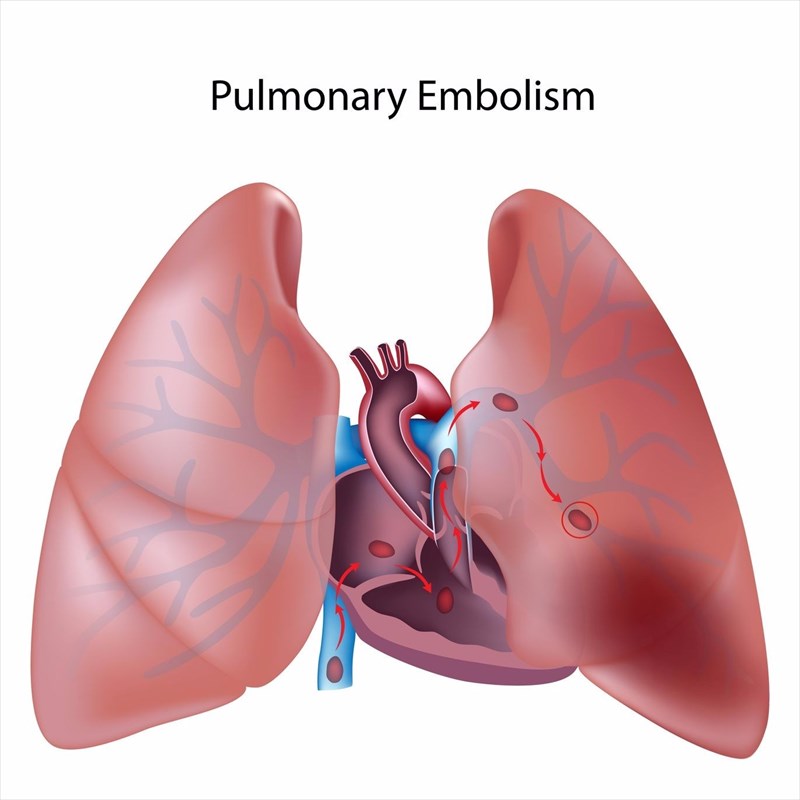
- Pulmonary embolism (PE): One of the main complication concerns with any DVT diagnosis is a PE. This condition is characterised as a blood clot that has travelled (usually from the leg) to the lungs and thus results in a blood vessel blockage which can be potentially fatal (causing severe damage to the lungs and various other portions of the body). Warning signs include sweating, sudden shortness of breath, dizziness (or light-headedness due to low blood pressure), chest pain (especially while breathing in deeply, bending, eating or coughing), rapid breathing (even when at rest), rapid or irregular heart rate (heart palpitations), and the coughing up of blood. Any symptoms which develop suddenly must be attended to by a medical professional as soon as possible (potentially requiring emergency treatment). Breathing problems, high blood pressure in the lung arteries (pulmonary hypertension) and heart failure must be attended to urgently.
- Venous thromboembolism (VTE): This complication combines DVT and a pulmonary embolism (PE) and can rapidly become life-threatening. The condition can also include long-term complications of post-thrombotic syndrome and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. The presence of blood clots in the lower extremities along with the breaking off of a piece of a thrombus which enters the lungs at the same time characterise this condition. Collectively the condition is known as venous thromboembolism. Warning signs combine symptoms of both conditions, and must be attended to on an emergency basis (i.e. urgent medical attention).
