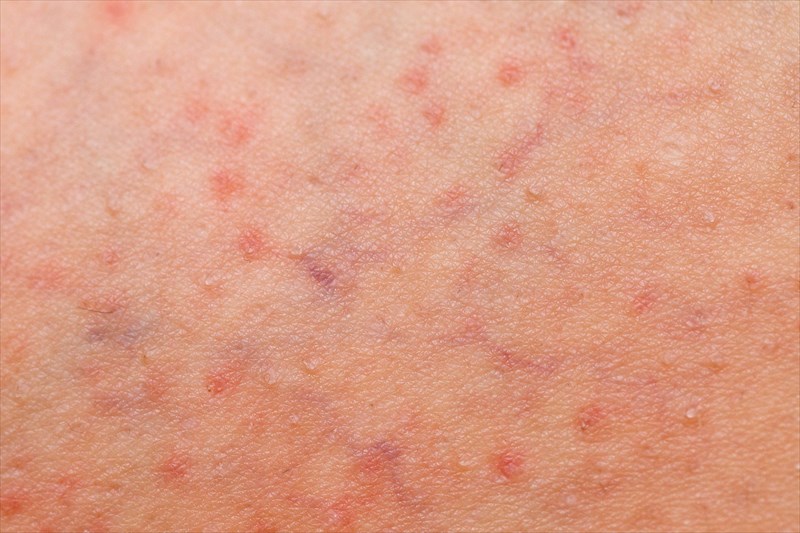
What is folliculitis?
Razor bumps. Barber’s itch. Hot tub rash. These painful red spots are common types of folliculitis, inflammation that occurs due to an infection of the hair follicles (the small pockets or cavities from which hair grows – i.e. at the root of hair). Every hair that grows on the body originates from its own hair follicle.
Folliculitis can occur anywhere on the body (i.e. all hair-bearing areas of the body), causing inflammation that is either superficial (occurring on the surface layers of the skin) or deep. The condition is most common in areas such as the legs, arms, chest (or abdomen area), back, head, face (the beard area in particular for men and when this occurs it is referred to as either pseudofolliculitis or tinea barbae), genitals and buttocks. Areas of the body that are more prone to friction are commonly affected by folliculitis breakouts and include the neck, armpits, thighs and buttocks.
Inflammation typically presents as a red spot with an overlying pustule (a red, tender bump containing pus at the tip – almost like a pimple) surrounding a central hair. Multiple bumps can resemble a rash or bout of acne (acne vulgaris). These bumps can be painful and itchy, resulting most often from infection (bacterial or fungal), physical injury (often due to friction), chemical irritation or occlusion (blockage). Bumps which linger can lose the pus-filled tip and will merely appear red and inflamed. They may also spread, affecting other areas of the body, as well as worsen, forming crusty sores which don’t appear to heal. Severe breakouts may result in scarring, which can lead to permanent hair loss.
Folliculitis is fairly common and not considered a serious inflammatory skin condition. Most mild breakouts (although often classified as acute) clear within a handful of days, and typically don’t require much medical intervention (if at all), resolving spontaneously. Simple self-care measures can easily clear up mild folliculitis without any long-term problems. Recurring (chronic) or more severe forms of the condition should be examined by a medical doctor, who can help clear up a breakout with the use of prescription medication (most often antibiotics although others may be prescribed depending on the underlying cause).
Other Articles of Interest
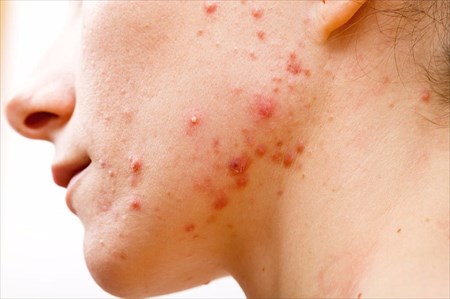
Acne
A common condition, acne can negatively affect a person's self-esteem. We break it down to help you understand it, and how to go about treating it...

Herpes Simplex Virus type 1 (Oral Herpes)
If you've ever experienced cold sores, you'll know how uncomfortable they are to experience. But do you know what causes them? Learn more about herpes simplex virus (HSV-1) here...

Herpes Simplex Virus type 2 (Genital Herpes)
Genital herpes is a common sexually transmitted infection that occurs in both men and women. There is currently no known cure, so how do you treat this condition?
