Symptoms of Gonorrhea
Some people with a gonorrhea infection may never develop noticeable symptoms (non-symptomatic carrier), while others will notice something wrong within a period of 2 to 14 days following exposure. It can take up to 30 days for an infection to develop in some people. A non-symptomatic carrier is still contagious, even without tell-tale signs of infection and can still pass on the infection.
Gonorrhea affects the genital tract of both men and women but can also show signs in other parts of the body. These include:
- The rectum: A pus-like discharge from the rectum, anal itching and strain during bowel movements.
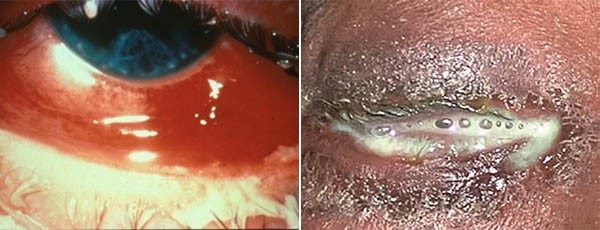
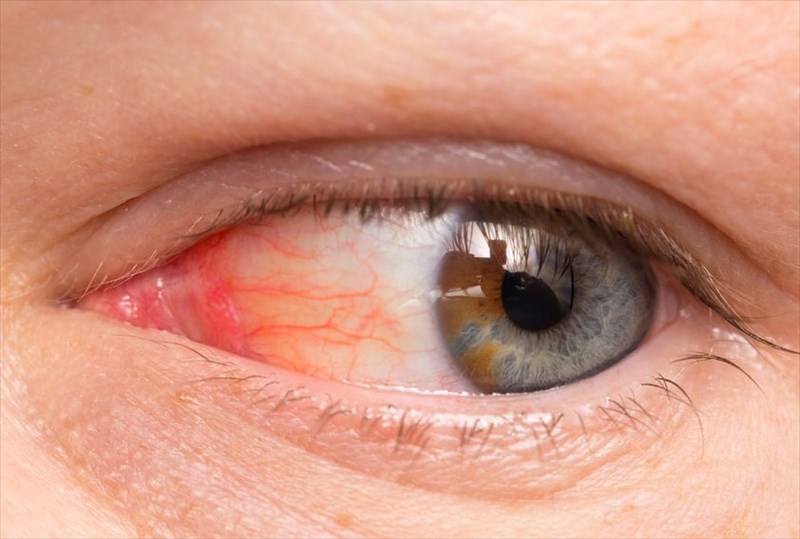
- The eyes: Sensitivity to light, pain or discomfort in the eyes, infection and a pus-like discharge from one or both eyes (this is known as gonococcal conjunctivitis).
- The throat: Sore and swollen lymph nodes in the neck.
- The joints: Bacteria can infect one or more joints in the body (septic arthritis) and cause warm, red, swollen and extremely painful symptoms, especially when you move (or are mobile).
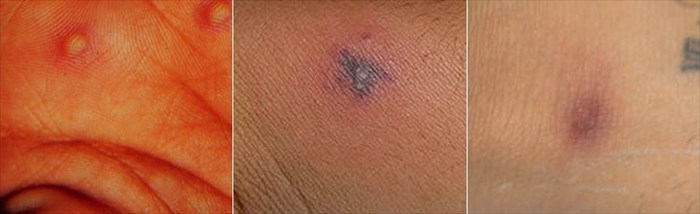
- The skin: If the bacteria that causes gonorrhea spreads it is referred to as a disseminated gonococcal infection (DGI) and can cause multiple skin lesions.
Symptoms of gonorrhea in men
It can take up to several weeks for men to develop noticeable symptoms, but typically an infection can begin to show signs a week following its transmission.
One of the first signs a man may notice when he has gonorrhea is a burning or painful sensation when urinating. This symptom is typically accompanied by any or more of the following:
- Urgency or increased frequency of urination
- Swelling or inflammation at the opening of the penis
- A white, yellow, beige or greenish pus-like discharge (‘the drip’) from the penis
- Swelling, pain or discomfort in the testicles (causing an epididymitis)
- A sore throat (this symptom is often persistent) or burning sensation (commonly experienced due to oral sex)
- Swollen glands in the throat (commonly experienced due to oral sex)
- Conjunctivitis (red and itchy eyes, commonly referred to as 'pink eye')
A gonorrhea infection will remain in the body for several weeks after any of the abovementioned symptoms show up and undergo treatment. It is rare, but gonorrhoea can cause further damage to the urethra and testicles or spread to the prostate.
Symptoms of gonorrhea in women
Women tend to experience mild symptoms which may be similar to those of other illnesses, such as vaginal yeast or bacterial infections. This can often make this STD more difficult to identify in the diagnosis process.
Many women don’t develop any symptoms, but the following noticeable signs of this STD are:
- A watery, creamy or greenish vaginal discharge
- An increased urgency to urinate (and more frequently than normal) as well as a burning or painful sensation when urinating (which is why Gonorrhea is often mistaken for a urinary tract infection).
- Heavier menstrual periods or spotting (bleeding between periods)
- A sore throat - Swollen glands and a burning sensation in the throat (commonly experienced as a result of oral sex)
- Sexual intercourse that is painful
- Spotting after sexual intercourse
- A sharp pain in the lower abdomen or pelvis
- Swelling of the vulva (vulvitis)
- Conjunctivitis (red and itchy eyes, commonly referred to as 'pink eye')
- Fever
Causes of gonorrhea
Neisseria gonorrhoeae is a contagious bacterium that easily grows and multiplies in the mucus membranes of the body. Bacteria favour warmth and moist areas for growth, and thus easily infect the reproductive tract (cervix, uterus and fallopian tubes), urethra, mouth, throat and anus.