- Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease
- What causes hand, foot and mouth disease?
- What are the symptoms of hand, foot and mouth disease?
- What are the complications and risk factors of hand, foot and mouth disease?
- Diagnosis, treatment and outlook for hand, foot and mouth disease
- FAQ about hand, foot and mouth disease
What are the symptoms of hand, foot and mouth disease?
The first symptoms of hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) usually present themselves between three to fives days after infection takes place and include:
- Mouth pain or a sore throat
- Loss of appetite
- A fever of 38.3°C (101°F) if present
- Malaise (general feeling of being sick or unwell)
Thereafter the following symptoms may occur:
- The development of painful sores on the inside of the mouth (these generally last for two to seven days)
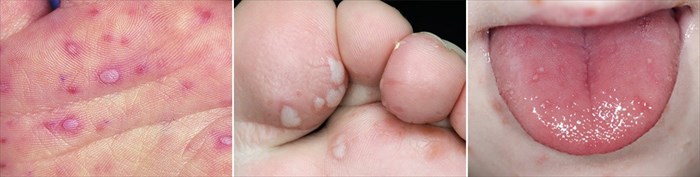
- Small, red sores or blisters transgressing into a rash on soles of the feet and palms of the hands and more rarely on the buttocks, genitals and limbs (arms and legs). These sores are not generally itchy or painful and heal withing three to four days.
- Irritability
Image: Hand, foot and mouth lesions present on the palms of the hands (left), soles of the feet (middle) and tongue (right)
When to see a doctor
HFMD is usually a minor illness that will result in a few days of relatively mild symptoms and signs. It is best if you phone your doctor if:
- Your child is drinking less than usual and / or cannot drink liquids due to their sore throat.
- Your baby or young child hasn't had a wet nappy (diaper) for four to six hours, or an older child has not urinated in six to eight hours. This is a sign of dehydration.
- Your child's symptoms progress after the first week of infection or they don't seem to be getting better.