Common unexplained type of lumps and swelling
An unexplained lump or swelling under the skin most commonly occurs in these areas of the body:
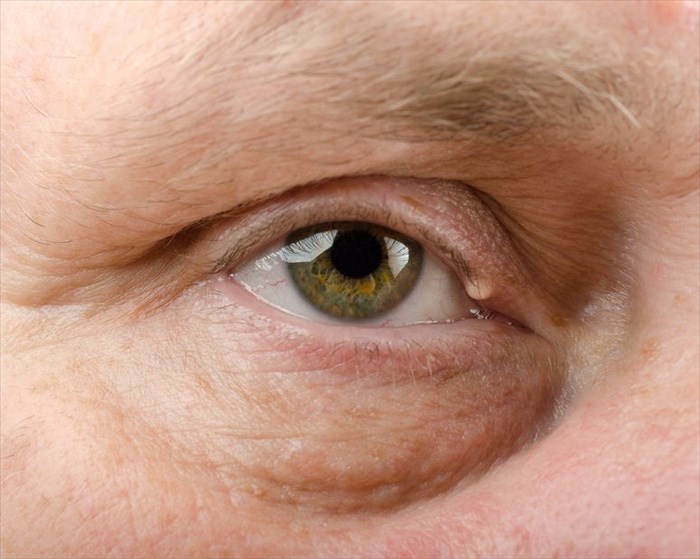
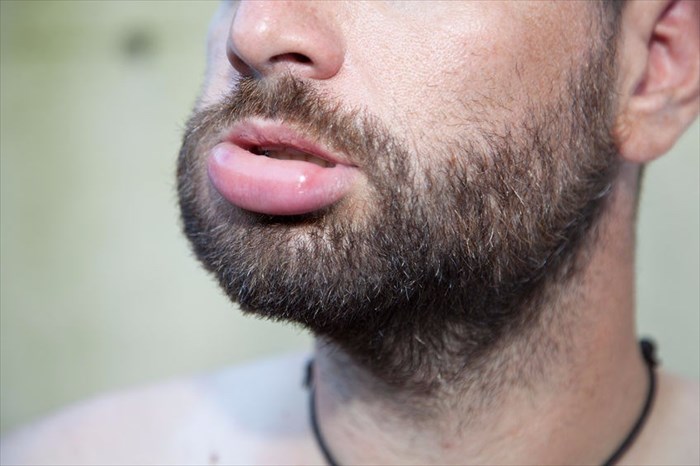
Facial swelling and lumps
Lumps or swelling can occur on the face as a direct result of injury. In instances where a lump or swelling cannot be explained, it may be as a direct result of another condition, infection or even allergic reaction.
Unexplained facial swelling or lumps can be a symptom of one of the following:
- Mumps: A contagious viral infection, commonly affecting children, mumps causes swelling in the parotid glands (side of the face). Swelling gives a person with the infection a distinctive 'hamster face' appearance. Along with swelling a person may experience symptoms of headaches, joint pain and may run a high fever a few days before noting any changes to their face.
- Allergic reactions: Many types of allergies can cause a swelling reaction, such as angioedema in the deeper layers of the skin. For instance, an allergy to peanuts or even medications can trigger swelling under the skin. Angioedema normally isn’t too serious, but it can be a recurring problem for some. (2) Where breathing difficulties are noted as well, this type of allergic reaction can be life-threatening and must be attended to by a medical professional immediately.
- A dental abscess: When a collection of pus caused by a bacterial infection forms on the inside of the teeth, in the gums or even in the bone structure surrounding the teeth, swelling in the side of the mouth can occur. An abscess that develops at the end of a tooth is known as a periapical abscess. An abscess in the gum is known as a periodontal abscess. Along with swelling both types of abscesses can be painful or not. In either instance, they should be treated by a dentist.
- A salivary gland stone: Saliva constantly flows from the salivary glands inside your mouth. When chemicals in saliva crystallise, forming a stone (salivary calculi) in the duct (tube), it causes a blockage of flow in the salivary gland. This results in swelling near the jaw, often accompanied by some degree of pain too.
Lumps and swelling in the neck or throat
Common types of swelling or lumps are:
- Swollen lymph glands: Swelling in the lymph glands is typically a sign of infection. Colds, flu or glandular fever (also known as infectious mononucleosis, or "mono") are common infections with symptoms of swelling. Swollen glands tend to subside once the cause of the infection is treated and cleared. Lymph glands (or lymph nodes) can sometimes have a more serious cause and will require medical assessment and appropriate treatment.
- Cysts: A cyst is a fluid-filled lump that is often harmless and may heal without any need for treatment at all. (3) Harmless cysts, when pressed with one's finger (palpated), often feel like a pea under the surface of the skin. If accompanied by pain or if the lump feels hard when pressed, it is advisable to see a medical professional for assessment.
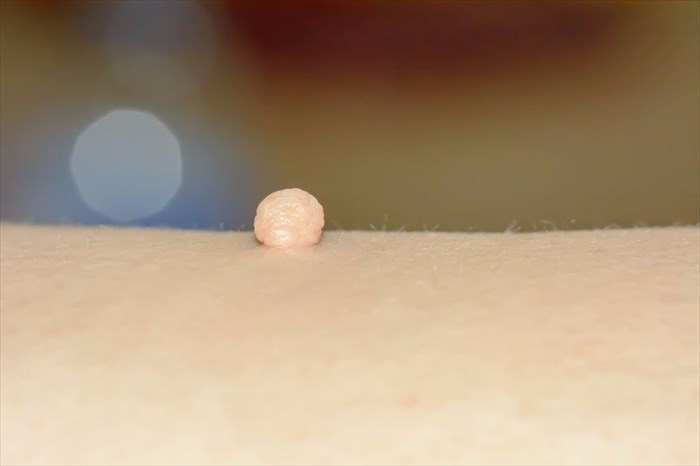
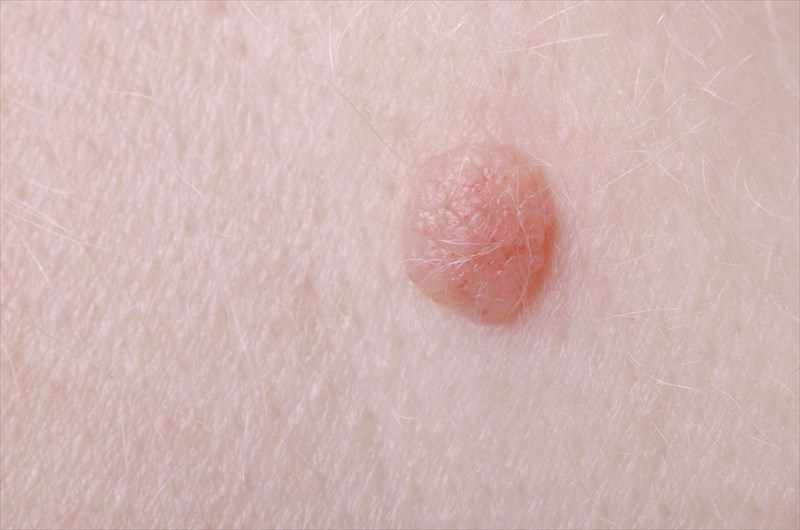
- Skin tags: These are soft wart-like, skin-coloured growths that hang off the skin and feel knobbly to the touch. Common, skin tags are most often harmless and can vary in colour and size – from as little as a few millimetres, up to 5 centimetres wide. Skin tags can also occur in the armpits, around the groin area, under the breasts, in the folds of the buttocks, and even grow on the eyelids.
- A goitre: This is an abnormal swelling of the thyroid gland (a butterfly-shaped gland in the neck) which results in a lump in the front of the neck. This lump will move up and down the neck as you swallow. The thyroid gland, located just in front of the windpipe (trachea) produces thyroid hormones which help to regulate metabolism in the body, as well as other chemical processes. The size of a goitre varies from person to person, but in most cases, the occurrence of swelling is small and usually doesn’t cause any other symptoms. If other symptoms such as coughing, a tight feeling in the throat, changes to your voice, or difficulties with swallowing or breathing occur, it is best to consult your doctor.
Lumps on the back, shoulder, chest or arm and armpit
Lumps and swelling that most often occur on these areas of the body are:
- Lipoma and cysts: Cysts can resemble a lipoma as both contain fluid (usually pus). The difference is that a cyst forms closer to the surface of the skin than lipoma (which occurs deeper under the skin) and are firm to the touch.
- Swollen lymph glands: Lumps that occur as a result of a swollen lymph gland commonly develop in the armpit. Swelling is usually as a response to some form of infection in the body, often accompanied by other symptoms. Glands in the armpit can swell up to a few centimetres in size, but usually go down when the cause of the infection is treated. Swelling in the lymph glands can sometimes be more serious, although it is fairly uncommon for the lump to be diagnosed as lymphoma (a form of cancer).
- Skin tags
Lumps on the hand, wrist or fingers
Common lumps on the hand, wrist or finger include:
- Ganglion cysts: This type of cyst forms around the joints and tendons and can commonly appear at the back of the wrist. The cyst contains a thick jelly-like fluid which feels smooth and soft under the skin. These types of cysts are common among those suffering an injury to the joint or tendon. These can be left if there is no presence of pain or discomfort, as they often disappear with no need for treatment. (4)
- Warts: These are small rough lumps that develop on the hands, often as a result of the human papilloma virus (HPV). Warts are contagious, but usually harmless and generally clear up without treatment.
Lumps in the breast
It is increasingly common for lumps to occur in the breast, however, they have several causes (not just breast cancer). Any unusual changes to the breasts are cause for concern and should be checked as soon as possible by a physician. Common causes of lumps found in the breast are:
- Mastitis: Breast tissue becomes swollen and painful as a result of inflammation. Sometimes mastitis is caused by an infection in the breast. It is also fairly common among breastfeeding women in the first three months following the birth of their baby. If breastfeeding is found to be the cause, this type of swelling or inflammation may be referred to as lactation mastitis or puerperal mastitis. Where breastfeeding isn’t the likely cause, periductal mastitis may be diagnosed.
- Enlarged milk ducts
- A fibroadenoma (non-cancerous growth)
- Cysts
- Skin tags: These can occur on the overlying breast skin or the nipple.
- Lipoma: These are soft, fatty lumps that form under the skin. Lipomas form as a result of an overgrowth of fat cells in the body and feel ‘doughy’ to the touch. If small and painless, these lumps are generally harmless and benign (non-cancerous), and can be left alone. Lipomas can grow anywhere in the body where there is the presence of fat cells, but are more commonly found around the shoulders, neck, chest, arms, thighs, back and buttocks. Lipomas range from the size of a pea to a few centimetres wide. Lipomas tend to develop deeper inside the body, making them more unnoticeable.
Lumps in the groin area
Common causes of lumps in this area of the body are:
- Cysts
- Swollen glands
- Hernia: This occurs when an internal part of the body between the chest and the hips, pushes through a weakeness in the muscle or surrounding tissue wall. Most experience very few symptoms, but swelling or lumps in the abdomen (stomach) or groin area are common complaints. Lumps often shift when you lie down, moving deeper inside the body. (5)
- An enlarged vein: This is known as saphena varix and is generally caused by a defective valve inside the vein. When you lie down, the lump tends to ‘disappear’ (move deeper inside the body).
- Genital warts: These are soft, fleshy growths on or around the genital or anal area that are usually as a result of a sexually transmitted infection (STI). Genital warts are a viral skin infection caused by the human papilloma virus (HPV). Usually painless, these warts are generally not serious and aren’t likely to have any effect on your fertility.
Lumps and swelling in the testicle
In general, most lumps found in the testicle aren’t cancerous or harmful. (6) Lumps and swelling is a fairly common symptom for boys and men, and have a number of different causes. Only a small percentage of testicular lumps, however, result in testicular cancer. The vast majority are as a result of other benign (non-cancerous) conditions and may not even require treatment. Any changes noted, however, should be checked by your physician, especially if any sudden or severely painful swelling occurs.
Swelling or lumps noted in the testicle can be:
- Varicoceles: Swollen veins inside the scrotum.
- Hydroceles: A build-up of fluid around the testicle.
- Epididymal cysts: Lumps are caused by a build-up of fluid in the epididymis (the coiled tube behind the testicles).
- Epididymo-orchitis: This is an inflammation of the epididymis and testicles.
- Inguinal hernias: Fatty tissue or part of the bowel pokes through the groin, causing the scrotum to become enlarged.
Lumps around the anus
Swelling or lumps around the anus (bottom) usually appear for one of the following reasons:
- Haemorrhoids (piles): This is a swollen blood vessel that hangs on the outside of the anus.
- Skin tags
- An abscess: A collection of pus caused by a bacterial infection, and which can be painful. Abscesses can develop anywhere on the body. A skin abscess develops under the skin. Internal abscesses can develop anywhere inside the body including in an organ or the space between organs.
- A rectal prolapse: This occurs at the end of the bowel where part of the rectum protrudes out of the anus.
- Genital warts
References:
2. niDirect Government Services. January 2018. Angioedema: https://www.nidirect.gov.uk/conditions/angioedema [Accessed 29.08.2018]
3. HealthDirect. May 2017. Cysts: https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/cysts [Accessed 29.08.2018]
4. HealthDirect. January 2018. Ganglion Cyst: https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/ganglion-cyst [Accessed 29.08.2018]
5. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. June 2014. Inguinal Hernia: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/inguinal-hernia [Accessed 29.08.2018]
6. Victoria State Government - Better Health Channel. August 2015. Testicular Cancer: https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/testicular-cancer [Accessed 29.08.2018]