- Molluscum Contagiosum
- What are the symptoms of molluscum contagiosum?
- What are the causes, risk factors and complications of molluscum contagiosum?
- How is molluscum contagiosum diagnosed?
- How is molluscum contagiosum treated?
- What is the prognosis and prevention of molluscum contagiosum?
- FAQ about molluscum contagiosum
How is molluscum contagiosum treated?
MC (molluscum contagiosum) will often heal naturally without treatment within six to 12 months, however, some people have been seen to continuously develop lesions for as long as four years. You are no longer contagious when all of your lesions/bumps have disappeared.
Your doctor may suggest that the lesions are removed. Removing the lesions can help to prevent the spread of them to others and other areas of your body as the MC virus is extremely contagious and the lesions can break easily.
The treatments for MC (molluscum contagiosum) can often be painful, because of this, your doctor may administer an anaesthetic before the treatment is issued in order to lessen any pain and discomfort. In some cases, your doctor may use a combination of various treatments. Bear in mind, treatment is often not needed for most patients.
The treatment options are described below:
Medications
It may be helpful for over-the-counter (OTC) or prescription drugs to be taken orally or applied directly to the bump/s. Some examples of these medications include:
- Retinoid topical creams – These include prescription gels and creams that contain retinoids. Retinoids are a class of compounds that are used to regulate and disrupt the cell growth and are often used in the treatment of acne. These include:
- Adapalene (Differin)
- Tretinoin (Retin-A, Atralin, Avita, Renova)
- Irritants – Medications in this category will aid in dissolving the lesions over a period of time. Some of these drugs will also form a blister under the lesion and cause the skin to lift, thus lifting the lesion off of your skin. These creams include ingredients such as salicylic acid or potassium hydroxide.
- Antiviral medication – This is often used to treat the infection and includes drugs such as Valtrex.
- Medication for children – Your doctor may give your child cimetidine (Tagamet) as this is a milder drug with fewer side effects.
- Immune booster - A new form of medication known as imiquimod (Aldara), aids in strengthening the immune system which can help to prevent the spread of the lesions in some cases.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs – These include drugs such as diclofenac gel which aids in suppressing
- Topical steroids – This class of drugs may help in relieving any itching associated with the lesions. These creams are applied to the areas of the skin that are itching and not the lesions directly. A hydrocortisone cream may also be used in cases where eczema (also known as atopic dermatitis and refers to irritated and inflamed skin) or dermatitis (skin inflammation) has developed.
Surgical options and other lesion-removal procedures
In some cases, your doctor may recommend that the lesions be removed. This can be achieved through:
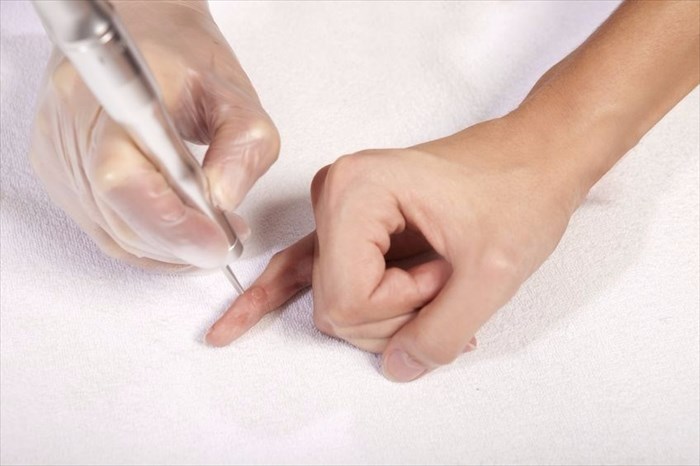
- Curettage – This procedure involves scraping the lesion off using an instrument known as a curet. A curet is spoon-shaped with a sharp edge. This is often done under local anaesthetic as it can be a rather painful procedure.
- Diathermy (burning) – This procedure makes use of an electrical device that is heated in order for the lesion to be burnt off.
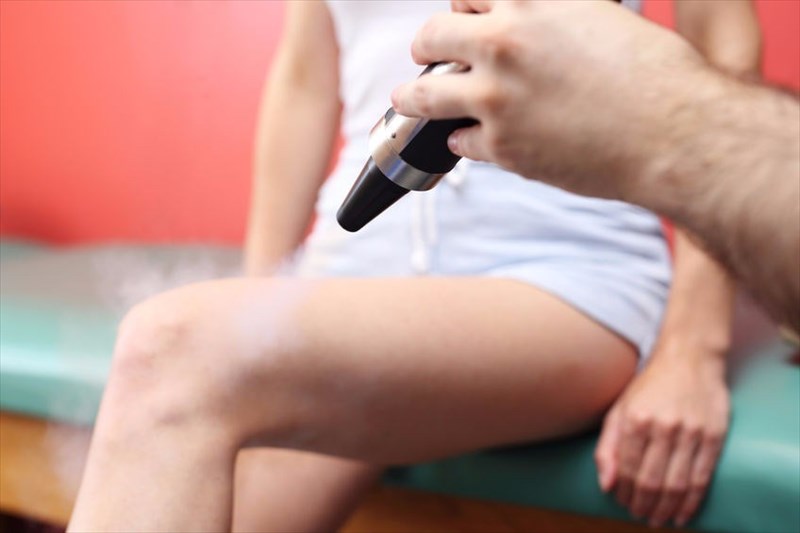
- Cryotherapy (freezing) – This procedure uses a pressurised liquid spray in order to freeze the lesion. Each lesion will be frozen for as long as ten seconds, or once an ice layer has formed over it and the surrounding skin. For some people, a number of sessions of freezing may be required in order for the lesions to be completely removed.
- Chemical treatment – This form of treatment involves the doctor dipping a sharp metal instrument into phenol or podophyllin. From here, each lesion will be pricked with the sharp device causing them to burst and have their contents emptied out. This may be painful and can lead to scarring.
- Laser therapy – This technique involves using narrow and intense beams of light to dissolve the lesions.
Molluscum contagiosum will not lie dormant in your body once the infection has completely cleared.This means it will not remain in your body and reappear, however, this is often the case with HPV (human papillomavirus).
Bear in mind, you are still able to be reinfected in the future should you come into contact with an infected person.
Does molluscum contagiosum have any home remedies?
There are a number of home remedies for molluscum contagiosum, however, there is little to no data on these to support their effectiveness in treating the lesions. It is advised that you first seek professional treatment from your doctor and discuss with him or her what your options of treatment are. If you are going to try any home treatments, then discuss these with your doctor during the same consultation.
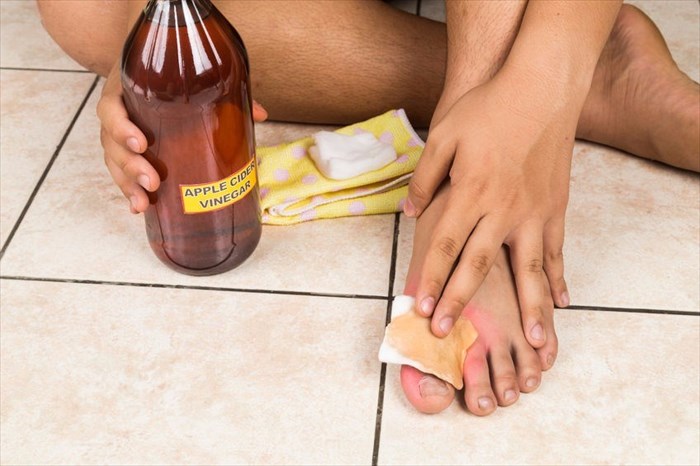
Some people have claimed that hydrogen peroxide, tea tree oil or apple cider vinegar applied directly to the lesion have shown positive results in ridding their skin of the papules. This is not to say that these are recommended. If you are seeking treatment, then speak to your pharmacist or doctor with regards to over-the-counter options such as ZymaDerm.


