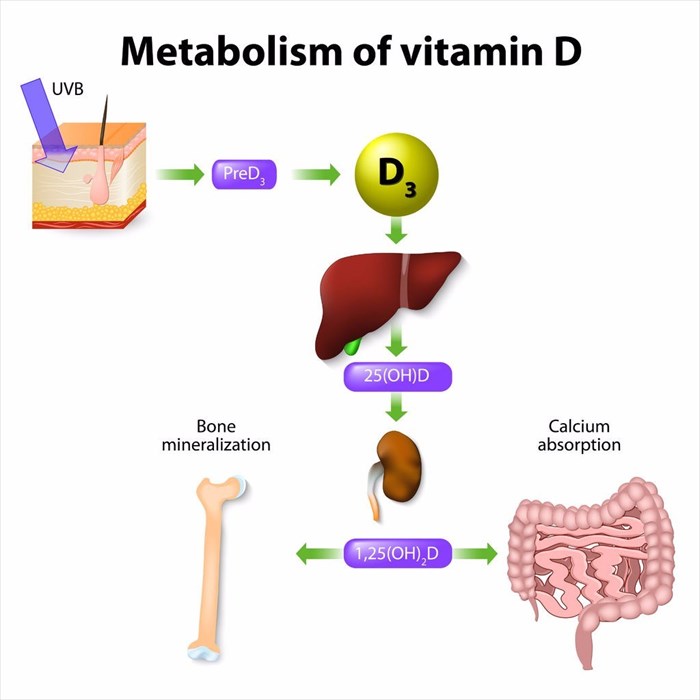
A healthy balance of vitamin D is essential for a variety of bodily functions. When your body obtains vitamin D from various sources (the sun, food and supplements), it goes through a variety of chemical processes. It is transported in through the bloodstream to the liver, where it is changed into a prohormone known as calcifediol1 (also known as calcidiol), which doctors use an indicator of the total amount of vitamin D in the body.
From there it is released into the blood and transported the kidneys which then produce the bioactive form of vitamin D.
This is referred to as calcitriol or activated vitamin D which is essentially a hormone.
Once activated, vitamin D is circulated back into your bloodstream and enters the cells of your body's where it attaches to the vitamin D receptors. Once attached, the activated vitamin D begins regulating minerals such as phosphorous and calcium in the bones, gut and blood. It also assists in the communication between cells throughout your body.
References
1. National Institute of Health. 11 February 2016. Vitamin D fact sheet for professionals. Available at: https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminD-HealthProfessional. Accessed: [25 October 2017]